Hate Speech
First Amendment Claim of Professor Fired Over Article Claiming Race-Based Genetic IQ Differences …
can go forward, rules a federal judge, denying Cleveland State University's motion to dismiss.
Some Critics of the Ruling Against Biden's Censorship by Proxy Have a Beef With the 1st Amendment Itself
"Disinformation" researchers alarmed by the injunction against government meddling with social media content admire legal regimes that allow broad speech restrictions.
Court: Public School Likely May Ban Student from Wearing "There Are Only Two Genders" T-Shirt,
notwithstanding the First Amendment.
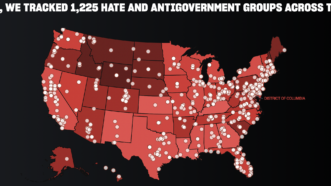
The SPLC Is Massively Overcounting 'Hate' Groups—and It's Not Just Moms for Liberty
At this rate, the Southern Poverty Law Center's notorious hate map might eventually describe everyone as an extremist.
Connecticut S. Ct. Sharply Limits State's "Racial Ridicule" Law
Prosecutors and police had read the law, which restricts "advertisements," as broadly banning racial slurs; the Connecticut court read it, as written, to restrict only commercial advertisements.
District Court Halts New York Law Forcing Online Platforms To 'Respond' to 'Hateful' Speech
"Today's decision is a victory for the First Amendment that should be celebrated by everyone who hopes to see the internet continue as a place where even difficult and contentious issues can be debated and discussed freely," said one attorney.
Studies Find Conservatives More Committed to Free Speech Online, Federalism
Plus: Government regulation of speech is on trial, biohackers flock to experimental charter city in Honduras, and more…
Davos Elites Warn That Disinformation Is an Existential Threat to Their Influence
At the World Economic Forum, Brian Stelter and panelists discuss why everything is Facebook's fault.
Teacher Can Proceed With First Amendment Lawsuit Over Threatened Punishment for Wearing MAGA Hat to Training
A defendant had argued that she could allow Black Lives Matters posters but forbid MAGA hats on the theory that, "While the Black Lives Matter poster is a symbol of cultural acceptance and inclusivity ... Mr. Dodge's MAGA hat is a symbol commonly associated with white supremacy and other anti-immigrant sentiments." No, says a Ninth Circuit panel.
Ninth Circuit Judge Urges Supreme Court "Not to Give Any First Amendment Protection for Racist Hate Speech"
“[G]overnment officials ... should not be unduly constrained in their attempts to regulate hate speech for the purpose of protecting the intended targets of said speech. This may require some refining of the Supreme Court’s prior guidance in its precedents.... For example, the Court could consider modifying the Brandenburg test to require only a probable and emerging threat of violence rather than imminent lawless action as a result of speech in order to regulate it.”
Ninth Circuit Upholds Expulsions for Off-Campus Abusive Speech That Targets Particular Students
“Students ... remain free to express offensive and other unpopular viewpoints [at least outside school], but that does not include a license to disseminate severely harassing invective targeted at particular classmates in a manner that is readily and foreseeably transmissible to those students.”
Hamline Student Newspaper (the Oracle) Removed Published Defense of Lecturer Who Showed Painting of Muhammad
"[T]rauma and lived experiences," the newspaper says, "are not open for debate."
Sifting Through the Twitter Files: Live With Nick Gillespie and Zach Weissmueller
Join Reason on YouTube and Facebook at 1 p.m. Eastern for a live analysis of the internal Twitter documents recently published by Matt Taibbi, Bari Weiss, and Michael Shellenberger.
Elon Musk Should Take a Clear Stand Against Censorship by Proxy
The most disturbing aspect of the “Twitter Files” is the platform’s cozy relationship with federal officials who demanded suppression of speech they considered dangerous.
Adam Schiff Attempts Censorship by Proxy, 'Demanding Action' To Suppress 'Hate Speech' on Twitter
Instead of debating whether the platform has been flooded by bigotry, Elon Musk should tell the congressman to mind his own business.
Journal of Free Speech Law: "Hate Speech, Holy Prophets, and Human Rights: The Struggle for Free Speech from 1945–2021,"
by Jacob Mchangama (Justitia), Heini Skorini (Univ. of Faroe Islands) & Mathias Meier (Justitia).
New York Forces Websites To Monitor 'Hateful' Speech. A New Lawsuit Says This Violates the First Amendment.
"The state of New York can't turn bloggers into Big Brother, but it's trying to do just that," said FIRE attorney Daniel Ortner.
Elon Musk Enforces Twitter's Ban on 'Hateful Conduct' As Critics Predict a Flood of Bigotry
The "free speech absolutist" is maintaining some content restrictions while loosening others.
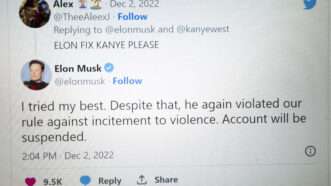
Kanye's Suspension Shows Musk Twitter Might Look a Lot Like…Old Twitter
Plus: Freedom's Furies, SCOTUS to take up student loan forgiveness plan, and more...
Twitter Was Toxic Long Before Musk Took Over
Plus: Hate speech is free speech, tax gap is stable, and more...
Kiwi Farms Is Back
The return of the trollish forum demonstrates the futility of bans on bad speech.
New Zealand P.M. Jacinda Ardern Peddles Government Censorship to an International Audience
The world’s politicians offer a friendly reception to attacks on free speech.
Germany's Criminalization of Online Offensiveness Shows the Perils of Weakening the First Amendment
A crackdown on insults, hate speech, and misinformation punishes dissenters who express themselves in ways that offend government officials.
Cloudflare Can Cancel Service to Terrible Websites Like Kiwi Farms. But Should It?
Cloudflare's decision brings up fundamental questions about how internet infrastructure companies should operate.
U.K.'s Online Censorship Bill Causes Far More Harm Than It Attempts To Prevent
The innocuously-titled Online Safety Bill threatens citizens' rights to privacy and to speak freely.
Racial Slurs Aren't "Obscene"
They thus can't be punished under a disturbing the peace law that bans "obscene language," though under the right circumstances they could be punished under separate provisions that generally ban "fighting words" (whether racially offensive or otherwise).
Federal Prosecutor Sets Up Hotline for Reporting, Among Other Things, People "Espousing … Hate-Filled Views"
"In Massachusetts, we have recently seen multiple incidents of groups espousing deeply offensive and hurtful ideologies displayed on our streets."
New Japanese Law Makes 'Online Insults' a Jailable Offense
Dedication to free speech is in short supply around the world, with Britain and Canada previously considering similar bills.
Court Rules for Student Free Speech as to Off-Campus "Me and the Boys Bout to Exterminate the Jews" Post
“Defendants cannot claim a reasonable forecast of substantial disruption to regulate C.G.’s off-campus speech by simply invoking the words ‘harass’ and ‘hate’ when C.G.’s speech does not constitute harassment and its hateful nature is not regulable in this context.”
New N.Y. Law Aimed at Getting Social Media Platforms to Restrict "Hateful" Speech
Its operative provisions just require social media platforms to create a mechanism for taking complaints about such "hateful" speech; but the title is "hateful conduct prohibited," and it's clear the legislature is trying to get social media platforms to restrict such speech more.
A response to the latest vilification campaign against the NRA
David Kopel at the National Firearms Law Seminar