Trump Administration Withdraws Proposed Obama Ban on Compensation for Bone Marrow
Thousands of patients who might have been helped died while rule was pending.
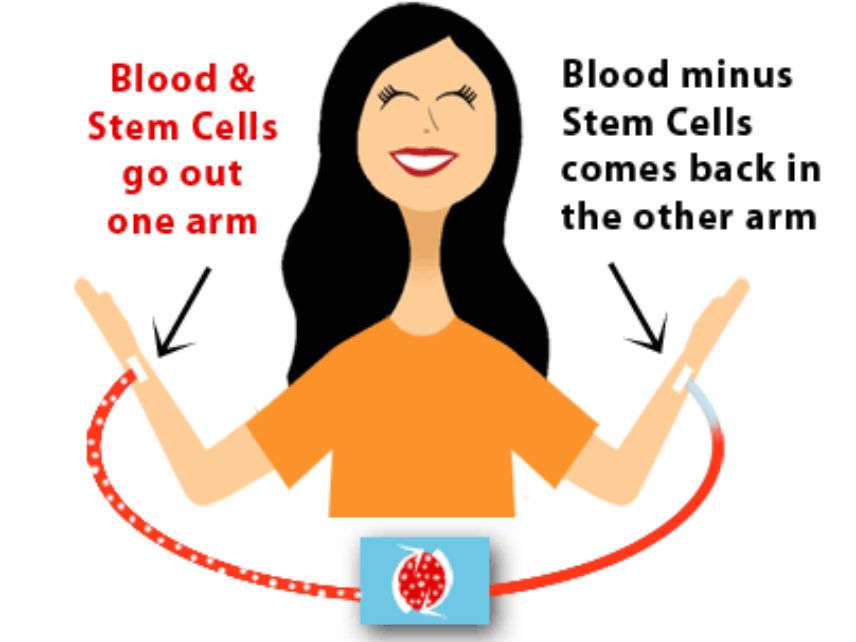
The Office of Management and Budget has withdrawn a proposed rule banning compensation for hematopoietic stem cells. In other words, you can get paid when someone harvests stem cells from your bone marrow.
Bone marrow transplantation is used to treat a variety of ailments, including aplastic anemia, sickle cell anemia, bone marrow damage during chemotherapy, and blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. In 1984, Congress passed the National Organ and Transplant Act, which outlawed compensation to the donors of solid organs like kidneys and livers. Oddly, the act also defined renewable bone marrow as a solid organ.
Originally, hematopoietic stem cells were obtained from bone marrow obtained by inserting a needle into donors' hip bones. Researchers later developed a technique in which donors are treated with substance that overstimulates the production of hematopoietic stem cells, which then circulate in their bloodstreams. In a process similar to blood donation, the hematopoietic stem cells are then filtered from the donors' blood. The red blood cells and plasma are returned to the donors.
More Marrow Donors, a California-based nonprofit, wanted to set up a system to encourage hematopoietic stem cell donations with $3,000 awards, in the form of scholarships, housing allowances, or gifts to charity. The Institute for Justice, a libertarian law firm, brought suit on their behalf, and in 2012 a federal appeals court sensibly ruled that the law's ban on compensation for solid organ donations did not apply to stem cells obtained from donors' bloodstreams. The Obama administration reacted by proposing a regulation defining stem cells obtained from blood as the equivalent of a solid organ.
Now the new administration has withdrawn the proposal.
"Banning compensation for donors would have eliminated the best incentive we have—money—for persuading strangers to work for each other," Jeff Rowes, a senior attorney with the Institute for Justice, says in a press release. "Predictably, the ban on compensation for blood stem cell donors created chronic shortages and waiting lists. During the past four years, thousands of Americans needlessly died because compensation for bone marrow donors was unavailable."
The system of uncompensated donation is falling far short of meeting patient needs. As the Institute for Justice notes:
At any given time, more than 11,000 Americans are actively searching for a bone marrow donor. According to the New England Journal of Medicine, Caucasian potential donors are available and willing to donate about 51 percent of the time; Hispanic and Asian about 29 percent; and African-American about 23 percent. Caucasian patients can find a matching, available and willing donor about 75 percent of the time; Hispanic about 37 percent; Asian-American about 35 percent; and African-American patients only about 19 percent of the time. This demonstrates the huge gap between the need for compatible donors and the supply.
This is even more true in the case of solid organs from live and brain-dead donors. Right now there are more than 116,000 Americans waiting for a life-saving transplant organ. My colleagues and I at Reason have been arguing for decades in favor of compensating live donors for kidneys and pieces of their livers and the next-of-kin of brain-dead donors for other solid organs. If researchers and entrepreneurs succeed in boosting bone marrow donations by implementing various compensation schemes, perhaps that will prompt Congress to repeal its ill-conceived ban on compensation for organs donated for transplant.


Show Comments (29)